ACCOMMODATION of eye
parallel rays of light coming from infinity are brought to focus on the retina, with accommodation being at rest.
However, our eyes have been provided with a unique mechanism by which we can even focus the diverging rays coming from a near object on the retina in a bid to see clearly. This mechanism is called accommodation.
In it there occurs increase in the power of crystalline lens due to increase in the
curvature of its surfaces.
At rest the radius of curvature of the anterior surface of the lens is 10 mm and that of posterior surface is 6 mm.
In accommodation, the curvature of the posterior surface remains almost the same, but the anterior surface changes, so that in strong accommodation its radius of curvature becomes 6 mm.
Mechanism of accommodation
According to von Helmholtz capsular theory in humans the process of accommodation is achieved by a change in the shape of lens as below:
• When the eye is at rest, the ciliary ring is large and keeps the zonules tense.
Because of zonular tension the lens is kept compressed (flat) by the capsule.
• Contraction of the ciliary muscle causes the ciliary ring to shorten and thus releases zonular tension on the lens capsule.
This allows the elastic capsule to act unrestrained to deform the lens substance. The lens then alters its shape to become more convex or conoidal.
The lens assumes conoidal shape due to configuration of the anterior lens capsule which is thinner at the center and thicker at the periphery.
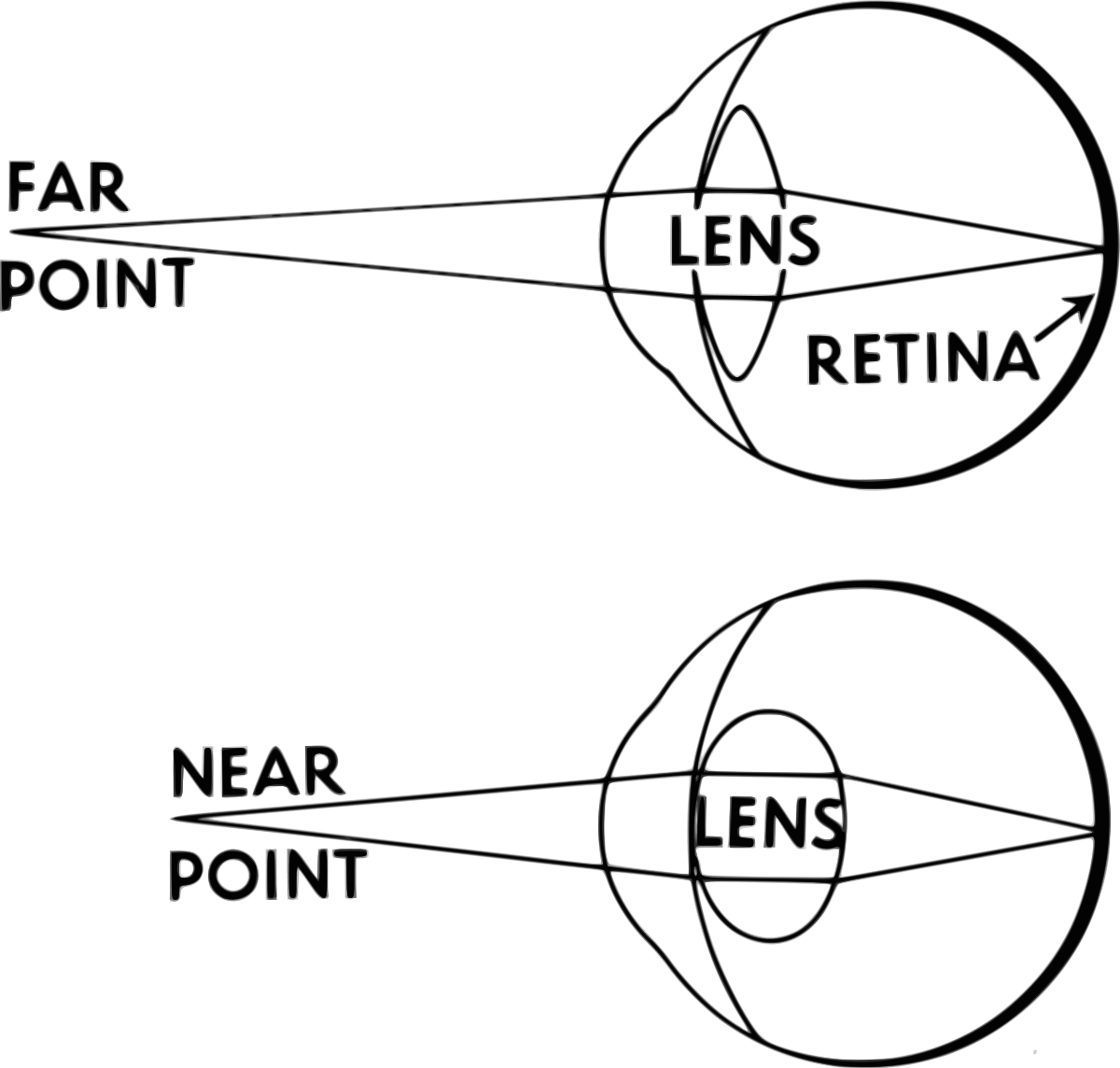
Far point and near point
The nearest point at which small objects can be seen clearly is called near point or punctum proximum and the distant (farthest) point is called far point or punctum remotum.
Far point and near point of the eye vary with the static refraction of the eye.
• In an emmetropic eye far point is infinity and near point varies with age.
• In hypermetropic eye far point is virtual and lies behind the eye.
• In myopic eye, it is real and lies in front of the eye .
Range and amplitude of accommodation
Range of accommodation.
The distance between the near point and the far point is called the range of accommodation.
Amplitude of accommodation.
The difference between the dioptric power needed to focus at near point (P) and far point (R) is called amplitude of accommodation (A). Thus A = P – R.
ANOMALIES OF ACCOMMODATION
Anomalies of accommodation are not uncommon.
These include:
(1) Presbyopia,
(2) Insufficiency of accommodation,
(3) Paralysis of accommodation, and
(4) Spasm of accommodation.